所謂 Static Link(靜態連結)──在 linking 階段針對未知 address 的 symbol 填入 address,把一堆 object file 黏在一起變成可執行檔。
沒了。(誤)
object file 是 compile 後的 binary 中間檔,它有多種 format,ELF 是其中之一。linking 主要是將其他 object file 中 symbol 的正確 address 填進 reference 到它的指令中,例如 object file A 的指令 reference 到 object file B 的 symbol x,link 前 object A 無法得知 x 的 address,link 時才會知道 x 正確的 address 並將之填進 object file A 的指令中。
Two-pass linking Static link 的流程是 two-pass linking,將 linking 分為兩個步驟:
分配 virtual address space
symbol resolution and relocation
1. 分配 virtual address space 合併多個 object file 成一個檔案。
掃描所有 object file,合併相同的 section,例如合併 a.o 跟 b.o 的 .text section。
linker 透過 object file 中的各種 table 得知各 section 的長度、屬性以及位置。
收集所有 object file symbol table 中的 symbol definition 跟 symbol reference 放到 global symbol table。
合併完 object file,各 symbol 的 virtual address 已經確定,linker 會計算 symbol 的 virtual address。
symbol 的 virtual address = 所在 section 合併後的 address + symbol 的 offset
2. symbol relocation and resolution static link 的重點。
compiler 不知道 reference 到別的 object file 中 variable 或 function 的 address,所以遇到其他 object file 的 symbol 時會塞假的 address 進 instruction。
利用 relocation table 將真正的 virtual address 填進 instruction 即為 symbol relocation。relocation table 記錄需要調整的 instruction 所在位置以及如何調整。每個需要 relocate 的 section 都有一個 relocation table,relocation table 也是 ELF 檔中的一個 section,如 .rel.text section 是 .text 的 relocation table。可以利用 objdump -r xxx.o 看 relocation table。
linker 由 global symbol table 得知 symbol 的 address,接著依據不同定址模式將 address 填進 instruction。所有 object file 中原本 undefined 的 symbol 經過 relocate 及 resolve 後應該要能在 global symbol table 中找到對應的 address,否則會出現 undefined reference 的 error。
Example 來點例子比較有 fu。
source foo.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 extern int sum;static int globalvar = 2 ;int foo (int a, int b) { static int staticvar = 1 ; sum = a + b; static int * p = &staticvar; p = ∑ }
sum 宣告成 extern,表示是其他檔案的 symbol,在 foo() 裡使用就是跨 object file 的 reference。
static 的 global 變數 globalvar 是只在這個 file 裡才看得到的變數。
main.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 extern int foo (int , int ) ;int sum = 1 ;int main () { foo(5 , 3 ); return 0 ; }
宣告 foo() 在別的檔案。
$ gcc -c foo.c main.c compile 成 object file。
$ ld foo.o main.o -e main -o foo link 兩個 object file,以 -e 指定 entry point。
PS:以上述簡化的 compile 及 link,程式會在跑到要結束的時候發生 segmentation fault,可能跟自己指定 entry point、未使用 C Runtime 處理開始及結束 process 有關。
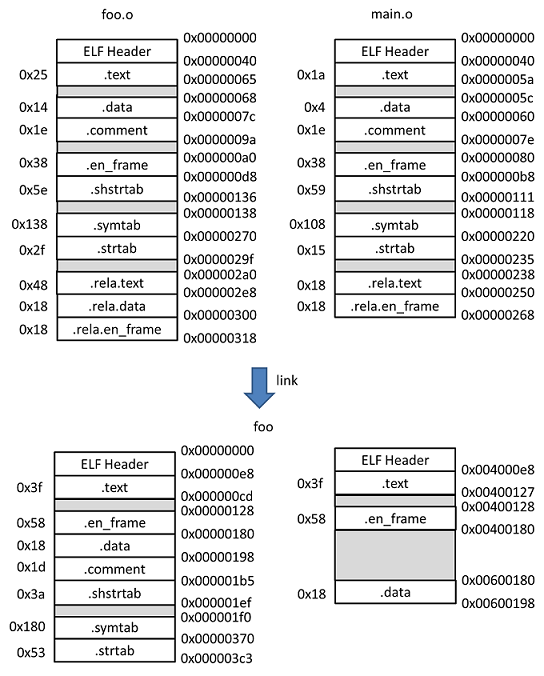
分配空間及 address 首先分配空間及 address,將多個 object file 裡相同的 section 放在一起並分配空間及 address,觀察三個檔案的 section:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 $ readelf -S foo.o There are 13 section headers, starting at offset 0x318: Section Headers: [Nr] Name Type Address Offset Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align [ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0 [ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000040 0000000000000025 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 1 [ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 000002a0 0000000000000048 0000000000000018 I 11 1 8 [ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000068 0000000000000014 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 8 [ 4] .rela.data RELA 0000000000000000 000002e8 0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 11 3 8 [ 5] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 0000007c 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1 [ 6] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000007c 000000000000001e 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1 [ 7] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000009a 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 1 [ 8] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000000a0 0000000000000038 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8 [ 9] .rela.eh_frame RELA 0000000000000000 00000300 0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 11 8 8 [10] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000000d8 000000000000005e 0000000000000000 0 0 1 [11] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 00000138 0000000000000138 0000000000000018 12 11 8 [12] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000270 000000000000002f 0000000000000000 0 0 1 $ readelf -S main.o There are 12 section headers, starting at offset 0x268: Section Headers: [Nr] Name Type Address Offset Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align [ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0 [ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000040 000000000000001a 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 1 [ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 00000238 0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 10 1 8 [ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000005c 0000000000000004 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 4 [ 4] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 00000060 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1 [ 5] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000060 000000000000001e 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1 [ 6] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000007e 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 1 [ 7] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000080 0000000000000038 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8 [ 8] .rela.eh_frame RELA 0000000000000000 00000250 0000000000000018 0000000000000018 I 10 7 8 [ 9] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000000b8 0000000000000059 0000000000000000 0 0 1 [10] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 00000118 0000000000000108 0000000000000018 11 8 8 [11] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000220 0000000000000015 0000000000000000 0 0 1 $ readelf -S foo There are 8 section headers, starting at offset 0x3c8: Section Headers: [Nr] Name Type Address Offset Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align [ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0 [ 1] .text PROGBITS 00000000004000e8 000000e8 000000000000003f 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 1 [ 2] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000400128 00000128 0000000000000058 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8 [ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000600180 00000180 0000000000000018 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 8 [ 4] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00000198 000000000000001d 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1 [ 5] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000001b5 000000000000003a 0000000000000000 0 0 1 [ 6] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 000001f0 0000000000000180 0000000000000018 7 10 8 [ 7] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 00000370 0000000000000053 0000000000000000 0 0 1
foo.o 跟 main.o 的 .text 以及 .data section 在 foo 合在一起啦!
relocation section 合併之後就能計算出 symbol 的 address,進入 static link 的重頭戲 relocation。
先看還沒 relocate 的 foo.o 的 symbol:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 $ readelf -s foo.o Symbol table '.symtab' contains 13 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 0: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND 1: 0000000000000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS foo.c 2: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 1 3: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 3 4: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 5 5: 0000000000000000 4 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 globalvar 6: 0000000000000008 8 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 p.1749 7: 0000000000000010 4 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 staticvar.1748 8: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 7 9: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 8 10: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 6 11: 0000000000000000 37 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 1 foo 12: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND sum
Num:symbol table array 的 index。
Name:st_name,symbol name。
Value:st_value,symbol value,該 symbol 的 address。
Size:st_size,表示所佔的大小。如果 symbol 是變數且在這個 object file 內,size 會有值,再根據有沒有 initialized 決定放在 .data 或 .bss section。global 跟 local static 有 initialized 的變數會在 compile 階段挖好空間、決定好 address,也就會在 executable file 中佔有空間。
Type 及 Bind 對應 st_info,GLOBAL 表示 global 可見,LOCAL 則表示在這個 compile unit 中可見。
Ndx:st_shndx,屬於哪個 section,UND 表示這個 symbol 還是 undefined。
globalvar 跟 staticvar 兩個變數都放在 .data section,foo 在 code section .text,sum 被宣告成 extern 則是 undefined 要等 link 的時候才知道在哪。
main.o 的 symbol:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 $ readelf -s main.o Symbol table '.symtab' contains 11 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 0: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND 1: 0000000000000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS main.c 2: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 1 3: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 3 4: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 4 5: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 6 6: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 7 7: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 5 8: 0000000000000000 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 3 sum 9: 0000000000000000 26 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 1 main 10: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND foo
sum 定義在 main.o 裡,foo 在 main.o 則是 undefined。
foo 的 symbol:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 $ readelf -s foo Symbol table '.symtab' contains 16 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 0: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND 1: 00000000004000e8 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 1 2: 0000000000400128 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 2 3: 0000000000600180 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 3 4: 0000000000000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 4 5: 0000000000000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS foo.c 6: 0000000000600180 4 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 globalvar 7: 0000000000600188 8 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 p.1749 8: 0000000000600190 4 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 3 staticvar.1748 9: 0000000000000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS main.c 10: 0000000000600194 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 3 sum 11: 0000000000600198 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 3 __bss_start 12: 000000000040010d 26 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 1 main 13: 00000000004000e8 37 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 1 foo 14: 0000000000600198 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 3 _edata 15: 0000000000600198 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 3 _end
link 後 symbol 填上 value,原本是 undefined 的 sum 跟 foo 都有各自的 address 跟所屬的 section。這個合併後的 symbol table 就是 global symbol table。
接著,linker 從 global symbol table 知道 symbol 的 address,並依據 relocation table 知道哪些幾個指令要改以及怎麼改。main.o 跟 foo.o 的 relocation table:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 $ readelf -r foo.o Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x2a0 contains 3 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000014 000c00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 sum - 4 00000000001b 000300000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .data + 0 00000000001f 000c0000000b R_X86_64_32S 0000000000000000 sum + 0 Relocation section '.rela.data' at offset 0x2e8 contains 1 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000008 000300000001 R_X86_64_64 0000000000000000 .data + 10 Relocation section '.rela.eh_frame' at offset 0x300 contains 1 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000020 000200000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text + 0 $ readelf -r main.o Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x238 contains 1 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 00000000000f 000a00000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 foo - 4 Relocation section '.rela.eh_frame' at offset 0x250 contains 1 entries: Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend 000000000020 000200000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text + 0
offset 欄位表示需要 relocate 的 instrcution 所在位置,如 foo.o 的 0x14 是需要 sum address 的位置。
修正 address 的方式依據 instruction 而定。簡單分成相對定址 跟絕對定址 ,可由 relocation entry 的 type 知道是哪種定址模式。相對定址填入相對下一個指令 address 的 offset,絕對定址填入 symbol 的絕對 address,所以執行檔中有以 offset 跟絕對 address 得到 symbol address 的 instruction。R_X86_64_PC32 屬於相對定址,R_X86_64_32S 屬於絕對定址。看看 link 後會 instruction 怎麼改變:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 $ objdump -d foo.o Disassembly of section .text: 0000000000000000 <foo>: 0: 55 push %rbp 1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 4: 89 7d fc mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp) 7: 89 75 f8 mov %esi,-0x8(%rbp) a: 8b 55 fc mov -0x4(%rbp),%edx d: 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%eax 10: 01 d0 add %edx,%eax 12: 89 05 00 00 00 00 mov %eax,0x0(%rip) # 18 <foo+0x18> 18: 48 c7 05 00 00 00 00 movq $0x0,0x0(%rip) # 23 <foo+0x23> 1f: 00 00 00 00 23: 5d pop %rbp 24: c3 retq $ objdump -d main.o Disassembly of section .text: 0000000000000000 <main>: 0: 55 push %rbp 1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 4: be 03 00 00 00 mov $0x3,%esi 9: bf 05 00 00 00 mov $0x5,%edi e: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 13 <main+0x13> 13: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax 18: 5d pop %rbp 19: c3 retq $ objdump -d foo Disassembly of section .text: 00000000004000e8 <foo>: 4000e8: 55 push %rbp 4000e9: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 4000ec: 89 7d fc mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp) 4000ef: 89 75 f8 mov %esi,-0x8(%rbp) 4000f2: 8b 55 fc mov -0x4(%rbp),%edx 4000f5: 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%eax 4000f8: 01 d0 add %edx,%eax 4000fa: 89 05 94 00 20 00 mov %eax,0x200094(%rip) # 600194 <sum> 400100: 48 c7 05 7d 00 20 00 movq $0x600194,0x20007d(%rip) # 600188 <p.1749> 400107: 94 01 60 00 40010b: 5d pop %rbp 40010c: c3 retq 000000000040010d <main>: 40010d: 55 push %rbp 40010e: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 400111: be 03 00 00 00 mov $0x3,%esi 400116: bf 05 00 00 00 mov $0x5,%edi 40011b: e8 c8 ff ff ff callq 4000e8 <foo> 400120: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax 400125: 5d pop %rbp 400126: c3 retq
compile foo.c 跟 main.c 時 compiler 不知道 reference 到外部 symbol 的 address,在 instruction 中填入 0,link 才填入真正的 address。
foo.o 的 instruction 從
1 2 3 12: 89 05 00 00 00 00 mov %eax,0x0(%rip) # 18 <foo+0x18> 18: 48 c7 05 00 00 00 00 movq $0x0,0x0(%rip) # 23 <foo+0x23> 1f: 00 00 00 00
變成
1 2 3 4000fa: 89 05 94 00 20 00 mov %eax,0x200094(%rip) # 600194 <sum> 400100: 48 c7 05 7d 00 20 00 movq $0x600194,0x20007d(%rip) # 600188 <p.1749> 400107: 94 01 60 00
mov 使用相對定址 access sum (0x600194),將下一個 instruction 的 address 0x400100 加上 0x200094 得到 sum 的 address,可從 symbol table 驗證。movq 使用絕對定址,由上 0x400107 可以看到 sum 的 address 直接寫進 instruction 了。之所以在 instruction 中數值看起來是反過來的,是因為 intel x86 CPU 使用 little-endian(Endianness wiki )。
main.o 則是
1 e: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 13 <main+0x13>
變成
1 40011b: e8 c8 ff ff ff callq 4000e8 <foo>
callq 指令要 call foo(),其中 e8 是指令本身,ffffffc8 是 offset,以二的補數來看是十進位 -56,所以 0x400120 - 0x38 = 0x4000e8,就是 foo() 的 address 啦。
Ref